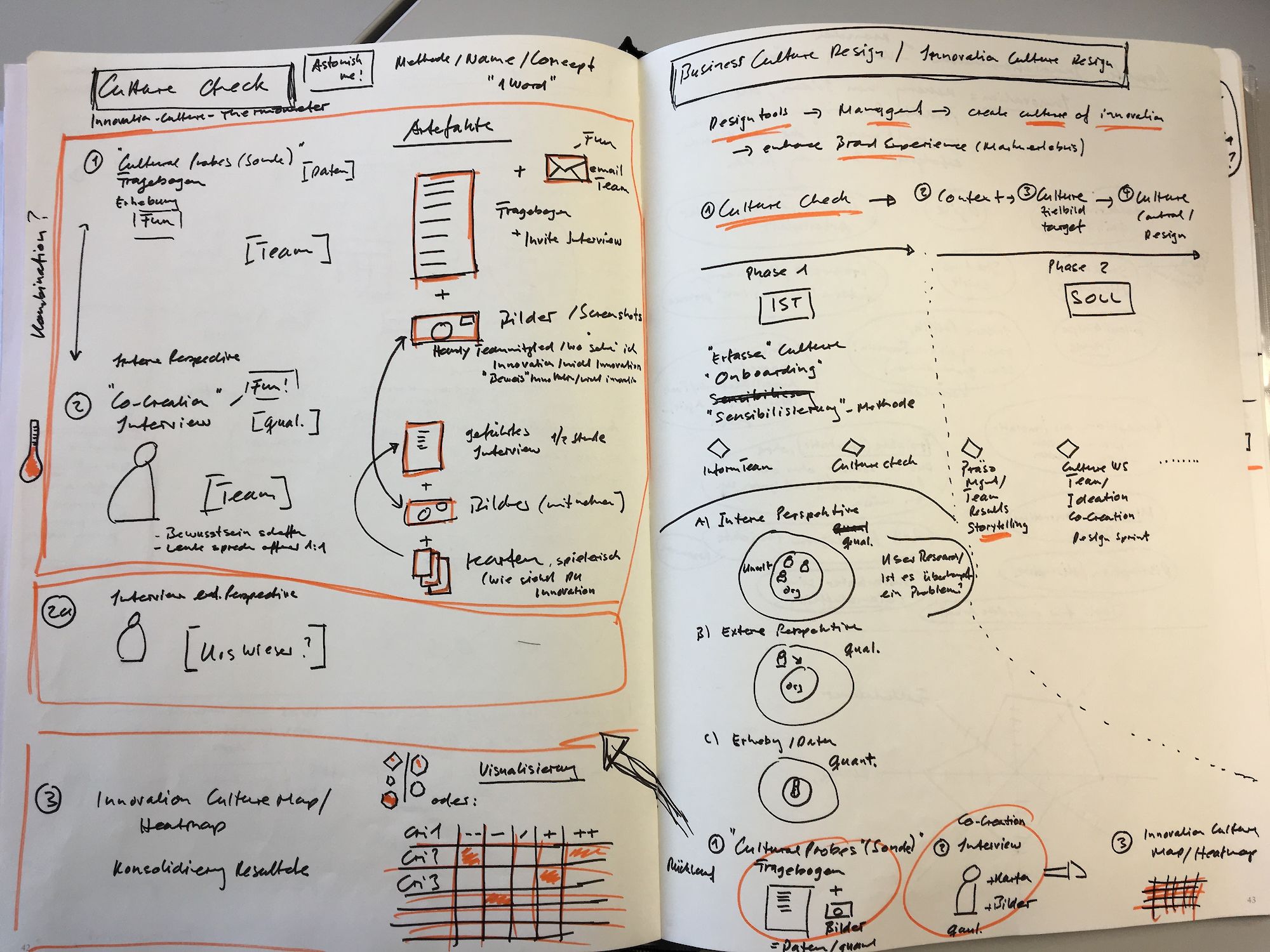
Starting point of the use case at hand is the desire to evaluate the current innovation culture in the bespoke team. The idea is to check the «temperature» with regards to the currently lived innovation culture with the individual team members (Phase 1 - Culture Check, focus of this method project), in order to provide the team lead with respective insights.
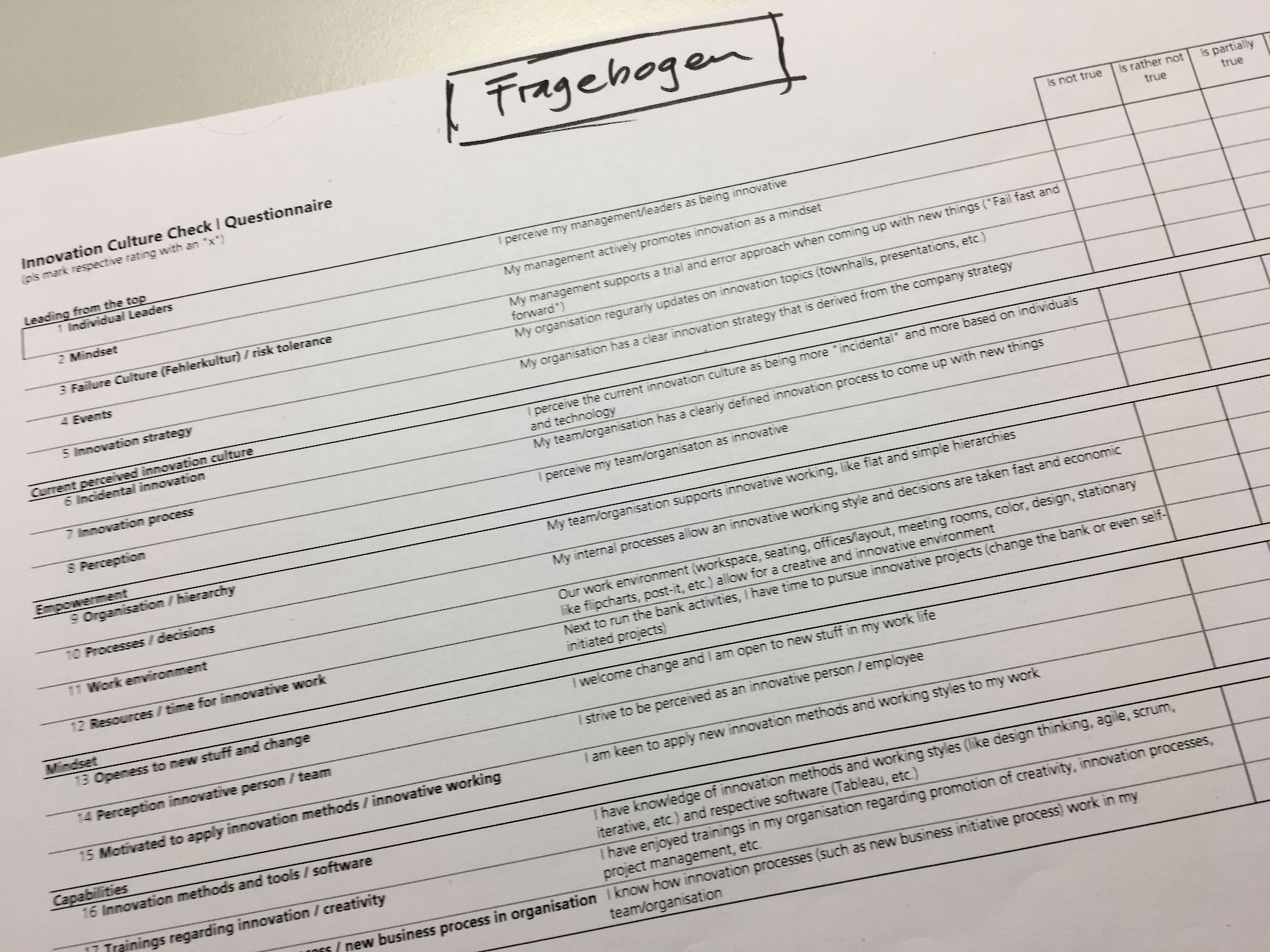
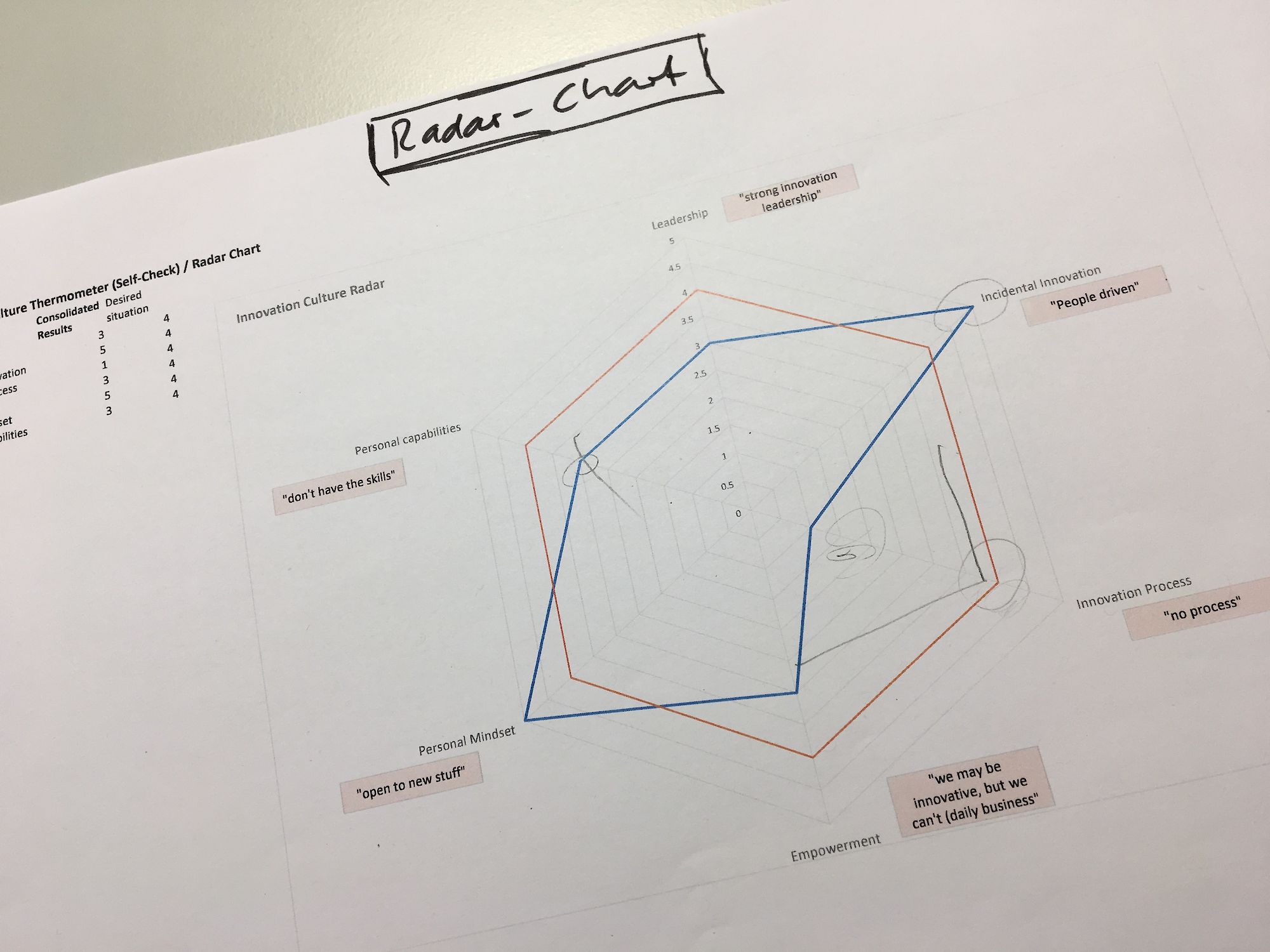
Approach: on one hand, the team members were requested to fill out a questionnaire concerning various innovation culture aspects and the manifestation in the team (Data, quantitative aspects). On the other hand, the author conducted individual 1:1 explorative interviews with the team members, to also learn more on the qualitative aspects of the current innovation culture. Finally, the consolidated results of the «temperature taking» were visualized in a radar chart, outlining the pain/gain areas of the current innovation culture aspects.
Methods: the main methods / tools applied were a questionnaire, an explorative interview (supported with pictures) and a radar chart as a visualization tool.
Results: the consolidated view of the results from the questionnaire and interviews show a good picture of the aspects of the innovation culture that are rather well developed in the team and the ones which are lagging behind. Despite the fact that some team members were hesitant to respond in a fully honest way (there is always the fear of personal repercussions when filling out surveys, although they are anonymous), a fairly clear trend could be identified which can be taken into the next phase of the innovation culture design process.
How might we check the current innovation culture of the business management team by providing the team lead with respective design tools?
The use case was performed with a business management team. The team covers various functions from business intelligence, classical business management, after sales and is embedded in the Client Coverage team for internal wealth management clients. The problem at hand was to check the current innovation culture within the team with appropriate methods/tools, to see whether in a second step an active design of the culture is necessary. The challenges were on one hand to design tools that capture the current innovation culture as accurate and «honest» as possible, on the other hand to create a comfortable environment for the interviewee to speak freely. The main people involved were the author (leading the process, taking on the role as «team leader») and the team members of the bespoke team.
Preparation use case
The initial idea of using the author’s old team as a use case for his method of checking the innovation culture has been discussed with the team lead, and has found a positive resonance. The topic of innovation is considered an important one, and the team leader has welcomed such a «status check» and potentially will continue the process with an active design of the desired innovation culture.
Preparation Design of tools
In a second step, the culture check tools (indented to be used as self-check tools) were prepared for the use case, using the questionnaire and interview method. The tools were considered appropriate for the use case.
Verify tools with Team Leader
The culture check tools have been presented to the team leader and have been discussed, and the team leader signed off on it.
Send out questionnaires to team members
The Questionnaire was then sent out to the 8 team members, accompanied with an email outlining the purpose and background of the culture check, as well as a guidance on how to fill out the questionnaire.
Support during questionnaire
The author provided support during the time when the team members filled out the questionnaire (they had a week to respond), and also advised that the questionnaire should be filled out rather quickly (to get more intuitive, honest answers).
Set up Interviews and meeting rooms
In parallel, the author has set up the individual interview dates and has reserved respective meeting rooms in the work area of the team members.
Receiving questionnaires & conduct interviews
The questionnaires were returned before the respective interview of the team members. Following, the individual interviews were conducted, first showing the interviewees some pictures regarding innovation culture, then following up with questions regarding certain aspects of the innovation culture based on the team members filled-out questionnaire, and always leaving enough room during the interview for the interviewee to download his view (gather additional information).
Evaluate results
After completion of all interviews, the author consolidated and evaluated the results and tried to identify the most important factors and trends of the innovation culture in the bespoke team (building clusters with post it’s).
Design innovation culture radar chart
To finish off, the author created the innovation culture radar chart (Thermometer) that visualizes the main results and that will be used for further discussion with the team lead and the team.
The innovation culture thermometer (self-check) method showed satisfying results to the author. The various aspects of the innovation culture of the team, that were checked with the method, were pronounced enough (either positively or negatively), so that the consolidated view provided a valuable picture of the current innovation culture in the team (pains and gains). While innovation culture aspects such as mindset, leading from the top and willingness are rated fairly positively, other aspects such as actually being able to work innovatively, the framework from the company (processes, organization, hierarchy), workload daily business and the work environment (works space, office set up) were rated rather negatively. To sum up the results, one is actually allowed («dürfen») to work innovatively, but actually cannot («können») to the preferred degree due to various constraints in the team/company.
From a methodical standpoint, the decision to perform individual interviews / questionnaires as opposed to conduct a team workshop to identify the innovation culture aspects was sensible. Even in the individual set up, the team members were at times hesitant to speak freely (fear of impact to their career if they do not say that team leader, team and environment is innovative); this behavior would even be stronger in a team workshop set up, where the members would even be more reluctant to voice their beliefs.
Further, the isolation of the team with regards to innovation showed difficult, as the team is strongly embedded in the overall organization, and the results do not only reflect the status of the team, but also the interwoven overall organization.